- Email : info@lifeclivut.eu
Notícias e Eventos
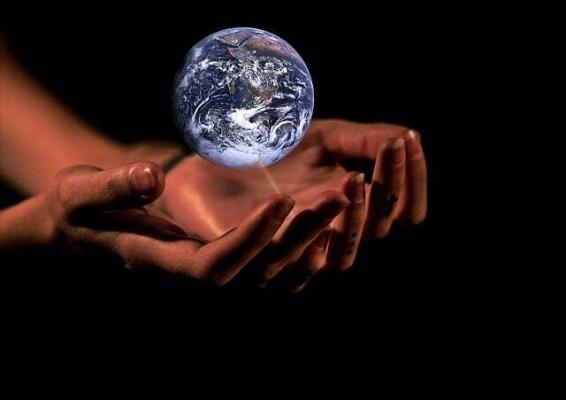
CLIMATE CHANGES
Climate change is defined as a series of long-term variations in temperatures and weather patterns.
Since the 19th century, human activities related to the construction of industries for primary goods have made it increasingly necessary to use fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas and this generates greenhouse gas emissions that act as a cloud around the Earth, retaining the heat of the sun and raising temperatures.
According to a report by the "Regional Information Center of the United Nations", the Earth is currently 1.1°C warmer and the last decade has been the warmest on record: drought is increasing, water scarcity, severe fires, floods, rising sea levels, melting ice and other catastrophic phenomena are only the beginning of a slow decay of the planet.
What can be the solutions?
For energy systems, switching from fossil fuels to renewables such as solar and wind will reduce emissions.
It is estimated, in fact, that by switching to these new energy systems by 2050, in the best expectations there will be almost zero emissions but at least half of the reductions will have to be made in 2030 to keep warming below 1.5 ° C.
The transition to clean energy, however, requires its costs, especially from governments and businesses, but climate inaction will have an even greater cost if immediate action is not taken.
Click here for download